“Are you tired of watching your business struggle with inefficiencies, wasteful practices, and disappointed customers? It’s time to transform the way you work! By improving your business processes, you can unlock a more efficient, productive, and profitable organization. In this article, we’ll show you how to streamline your operations, eliminate waste, and delight your customers. Get ready to take your business to the next level!”What Is Process Improvement
Driving Business Success
Process improvement is the unsung hero of business success. It’s the secret sauce that helps companies stay ahead of the competition, achieve their strategic objectives, and delight their customers. But what does this mean in real life? What Is Process Improvement
Let’s take the example of a busy coffee shop. Imagine you’re the owner, and you notice that the line is consistently long during morning rush hour. Customers are getting frustrated, and some are even leaving without making a purchase. By streamlining the order-taking process, training staff to work more efficiently, and implementing a digital ordering system, you can reduce wait times, increase customer satisfaction, and boost sales.
Or consider a software development company struggling with lengthy project timelines. By analyzing and optimizing their development process, they can reduce project duration, improve quality, and increase customer satisfaction. This leads to more repeat business, positive referrals, and a competitive edge in the market. What Is Process Improvement
In both cases, process improvement is the key to unlocking business success. It’s not just about cutting costs or increasing efficiency; it’s about creating a better experience for your customers and employees and setting your business up for long-term success. What Is Process Improvement
Guiding Principles of Process Improvement
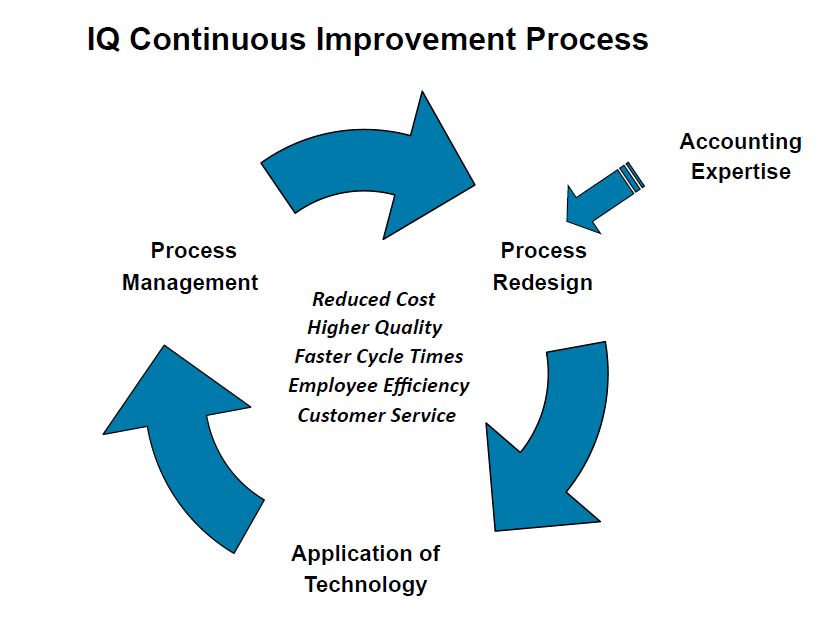
When it comes to process improvement, it’s easy to get caught up in the details. But to truly succeed, you need to keep your eyes on the prize – your customers, your employees, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Here are the guiding principles to keep in mind:
Customer-Centricity
Put yourself in your customers’ shoes. What do they want from your business? What problems do they need to be solved? By understanding their needs and pain points, you can design processes that deliver value and delight. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A healthcare provider streamlines their appointment scheduling process, reducing wait times and making it easier for patients to get the care they need. What Is Process Improvement
Employee Empowerment
Your employees are the ones on the front lines, dealing with customers and carrying out processes every day. Encourage them to speak up, share ideas, and take ownership of improvement efforts. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A manufacturing team identifies a bottleneck in production and works together to implement a more efficient solution, increasing productivity and job satisfaction. What Is Process Improvement
Continuous Improvement
Process improvement is not a one-time event, but a journey. Encourage a culture of ongoing learning, experimentation, and iteration. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A software company adopts an agile development approach, regularly gathering customer feedback and iterating on its product to stay ahead of the competition. competition.nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Proven Approaches to Process Improvement

When it comes to process improvement, it’s not necessary to reinvent the wheel. Leveraging established frameworks and methodologies can provide a structured approach, saving time and resources. Let’s explore three popular options:
Lean
Originating in the manufacturing industry, Lean focuses on eliminating waste, optimizing flow, and improving quality. By applying Lean principles, businesses can streamline processes, reduce errors, and increase customer satisfaction.
Example: A hospital implements Lean to reduce patient wait times, resulting in a 30% decrease in wait times and a significant improvement in patient satisfaction. What Is Process Improvement
Six Sigma
This data-driven approach aims to reduce defects and variations, resulting in high-quality processes. Six Sigma uses belt-based certifications (White, Yellow, Green, Black) to denote expertise.
Example: A financial services company uses Six Sigma to improve its claims processing, achieving a 99.9% accuracy rate and reducing processing time by 40%. What Is Process Improvement
Kaizen
This Japanese philosophy emphasizes continuous, incremental improvement. Kaizen encourages employee involvement, empowering teams to identify and address areas for improvement. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A retail chain adopts Kaizen, engaging employees in improvement initiatives that result in a 25% reduction in inventory costs and a 15% increase in customer satisfaction.
Uncovering Opportunities for Improvement
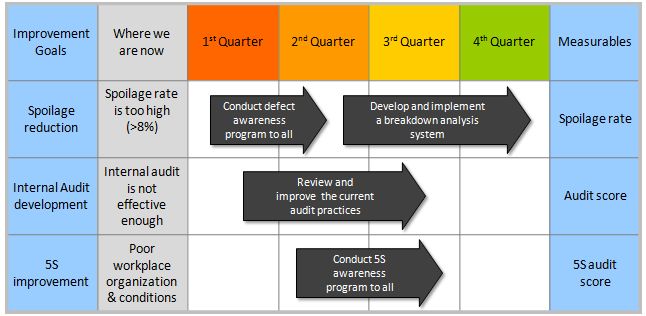
The first step in process improvement is understanding where you are today. It’s time to put on your detective hat and gather clues about areas that need attention. Here’s how: What Is Process Improvement
Data Analysis
Numbers don’t lie! Dive into your data to identify trends, patterns, and pain points. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A marketing team analyzes website metrics, discovering a high bounce rate on their landing page. This insight sparks a redesign, resulting in a 20% increase in conversions.
Stakeholder Feedback
Ask the people who matter most – customers, employees, suppliers – what they think. Their input can be invaluable. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A hotel chain surveys guests, revealing a desire for more flexible check-in times. By implementing a new check-in system, they boost customer satisfaction ratings by 12%.
Process Mapping
Visualize your processes to spot inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for streamlining. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A manufacturer maps their production process, identifying unnecessary steps that were adding days to their lead time. By eliminating these steps, they reduce production time by 30%.
Assessing the Current State

It’s time to look closely at your existing processes, warts and all. This is not about judging but about understanding. Think of it as a health check-up for your business. What Is Process Improvement
Process Evaluation
Take a step back and assess your processes objectively, considering:
- Strengths: What’s working well? What are you proud of?
- Weaknesses: Where are the pain points? What’s causing frustration?
- Opportunities: Where can you improve efficiency, reduce waste, or enhance customer experience?
Example: A restaurant owner evaluates their order fulfillment process, realizing that manual ordering is causing delays and errors. Switching to a digital system reduces wait times and increases order accuracy.
Identifying Inefficiencies
Look for common culprits like:
- Bottlenecks: Where are processes slowing down or getting stuck?
- Redundancies: Are there duplicate efforts or unnecessary steps?
- Waste: Where are resources being squandered or misused?
Example: A software developer identifies a redundant data entry process, automates it, and frees up 10 hours weekly for more strategic tasks.
Setting Goals for Success

Now that you’ve identified areas for improvement, it’s time to define what success looks like. Clear objectives, metrics, and targets will guide your process improvement initiatives and keep everyone focused on the prize.
SMART Goals
Make sure your objectives are:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
Example: A customer service team aims to “Reduce average response time to under 2 hours within the next 6 weeks” to improve customer satisfaction.
Metrics and Targets
Establish concrete metrics and targets to track progress:
- Quantitative: Reduce errors by 25% in the next quarter
- Qualitative: Improve customer feedback ratings by 15% in the next 6 months
Example: A manufacturing plant sets a target to “Increase production capacity by 10% within the next 9 months” to meet growing demand.
Human Touch
Remember, process improvement is about people, not just processes. Engage your team in the goal-setting process to foster ownership and motivation.
Example: A marketing team works together to define objectives, resulting in a shared sense of purpose and a 25% increase in productivity. What Is Process Improvement.
Designing and Refining Solutions

It’s time to get creative and develop new processes or improvements to existing ones! This is where the magic happens, and you start to shape the future of your business.
Idea Generation
Gather your team and brainstorm ideas for improvement. Encourage wild and ambitious thinking! What Is Process Improvement
Example: A retail team brainstorms ways to enhance the customer experience, resulting in an innovative loyalty program that increases sales by 15%.
Prototyping and Testing
Turn ideas into tangible prototypes and test them with real users. Iterate and refine based on feedback. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A software developer creates a minimum viable product (MVP) and tests it with a small group of customers, gathering valuable insights that inform the final product.
Process Redesign
Rethink and redesign existing processes to make them more efficient, effective, and enjoyable. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A healthcare provider streamlines their patient intake process, reducing wait times and improving the overall experience for patients and staff. What Is Process Improvement.
Human-Centered Approach
Remember, processes are designed for people, not just efficiency. Keep the human touch in mind when designing and testing solutions. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A bank develops a new online platform that prioritizes user experience, resulting in a 30% increase in online transactions and a 25% increase in customer satisfaction.
Implementing Change and Ensuring Success

The moment of truth has arrived! It’s time to put your carefully designed processes into action, equip your team with the necessary skills, and track progress. What Is Process Improvement
Rolling Out Changes
Introduce new processes or improvements to existing ones, communicating the benefits and rationale to your team. What Is Process Improvement
Example: A restaurant chain rolls out a new menu and preparation process, providing comprehensive training to all staff members.
Training and Support
Equip your team with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed. Offer ongoing support and feedback to ensure a smooth transition.
Example: A software company provides interactive training sessions and dedicated support teams to help employees adapt to a new project management tool.
Monitoring Progress
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and gather feedback to measure the success of your process improvements.
Example: A manufacturing plant implements a new quality control process, monitoring defect rates and gathering feedback from production staff to refine the process further.
Celebrating Successes
Acknowledge and celebrate the successes of your team members, reinforcing the behaviors and processes that drove positive change.
Example: A customer service team recognizes and rewards agents who consistently receive high customer satisfaction ratings, motivating the team to continue delivering exceptional service.
Assessing the Impact
The final step in the process improvement journey is to evaluate the impact of your efforts. This is where you get to see the fruits of your labor and make adjustments to further optimize your processes.
Metrics and KPIs
Track relevant metrics and KPIs to measure the success of your process improvements. Compare them to your baseline data to see the progress.
Example: A hospital tracks patient satisfaction scores, finding a 25% increase after implementing a new care coordination process.
Success Stories
Celebrate the successes and recognize the teams or individuals who made it happen. Share their stories to inspire others.
Example: A software company showcases a team that reduced bug resolution time by 40%, highlighting their innovative approach and collaboration.
Areas for Refinement
Analyze the data to identify areas that still need improvement. Refine processes further to achieve even better results.
Example: A retail chain analyzes sales data, finding that a new inventory management process improved stock levels but didn’t quite meet the target. They refine the process, resulting in a further 10% reduction in stockouts.
Continuous Learning
Process improvement is a journey, not a destination. Embed a culture of continuous learning, encouraging teams to keep innovating and improving.
Example: A manufacturing plant establishes a regular review process, encouraging teams to share lessons learned and best practices, driving ongoing improvement.
Building a Culture of Excellence

The final step in our process improvement journey is to make it a fundamental part of who you are as an organization. It’s time to embed a culture of continuous learning and innovation into the very DNA of your company.
Lead by Example
Leadership sets the tone. Demonstrate your commitment to process improvement and encourage your team to do the same.
Example: A CEO prioritizes process improvement, allocating dedicated resources and recognizing team achievements, inspiring a company-wide movement.
Empower Your Team
Give your team the autonomy to identify areas for improvement and provide the resources to make it happen.
Example: A marketing team is empowered to optimize their campaign processes, resulting in a 20% increase in lead generation.
Recognize and Reward
Celebrate successes and recognize team members who drive process improvement, reinforcing the behavior.
Example: A company introduces an “Improvement Champion” award, acknowledging employees who demonstrate exceptional process improvement skills.
Continuous Learning
Foster a culture of ongoing learning, providing training and development opportunities to stay ahead of the curve.
Example: A healthcare organization establishes a dedicated process improvement academy, offering regular workshops and training sessions.
Innovation Incubator
Create a safe space for experimentation and innovation, encouraging experimentation and learning from failures.
Example: A tech company sets up an innovation lab, where teams can explore new ideas and test prototypes, leading to breakthrough solutions.

