“Imagine a business where every effort counts, every resource is utilized, and every customer leaves satisfied. Welcome to the world of Lean management, a revolutionary philosophy that transforms the way organizations work. By slashing waste and maximizing value, Lean has been the secret weapon of industry giants and innovative startups alike. Want to know the secrets of this game-changing approach? Let’s dive in and explore the power of Lean!”What is lean
Lean's roots in the Toyota Production System and its adaptation across industries
In the 1940s, Kiichiro Toyoda, the founder of Toyota, faced a daunting challenge: how to produce high-quality cars with limited resources. He turned to his team, led by Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo, to develop a new approach. Thus, the Toyota Production System (TPS) was born.
TPS focused on two main goals:
- Eliminating waste (muda, in Japanese): reducing unnecessary steps, inventory, and defects.
- Improving flow (kaizen): continuously enhancing processes to create a smoother, more efficient workflow.
This innovative approach transformed Toyota into one of the world’s leading automakers. But Lean’s impact didn’t stop there. What is lean
From assembly lines to operating rooms
Today, Lean principles are applied in various industries, including:
- Healthcare: hospitals like the Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins use Lean to streamline patient care, reducing wait times and improving outcomes.
- Aviation: companies like Boeing and Airbus apply Lean to manufacture aircraft more efficiently and safely.
- Software development: tech giants like Google and Amazon use Lean to develop and launch new products quickly.
- Retail: companies like Walmart and Tesco use Lean to optimize supply chains and inventory management.
These organizations have discovered that Lean’s focus on value, waste reduction, and continuous improvement can lead to remarkable results, such as:
- Improved quality and safety
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
- Reduced costs and increased competitiveness
Eliminate waste, amplify value, and continuously improve
At its core, Lean is built on three guiding principles:
- Eliminate waste (muda): Get rid of anything that doesn’t add value to your customers or your business.
- Amplify value: Focus on what matters most to your customers and deliver it with excellence.
- Continuously improve (kaizen): Encourage a culture of ongoing learning and innovation.
These principles might sound simple, but they have a profound impact on how organizations operate. What is lean
The power of eliminating waste
Take the example of a hospital like the Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle. By eliminating waste in their processes, they reduced the average length of stay for patients by 25% and saved millions of dollars in the process.
Or consider the story of a small business like Lantech, a packaging company that reduced waste by 50% and increased productivity by 20% by streamlining its workflow. What is lean
Amplifying value in action
Companies like Amazon and Apple are masters at amplifying value for their customers. They understand what matters most to their customers – convenience, ease of use, and innovative design – and deliver it with excellence. What is lean
Continuous improvement in practice
At Toyota, continuous improvement is a way of life. Their employees are encouraged to identify and solve problems daily, resulting in thousands of small improvements that make a big difference.
These principles are not just theoretical – they have the power to transform organizations and improve people’s lives. By eliminating waste, amplifying value, and continuously improving, organizations can achieve remarkable results and stay ahead of the competition. What is lean
Value streams, continuous flow, pull production, and perfection
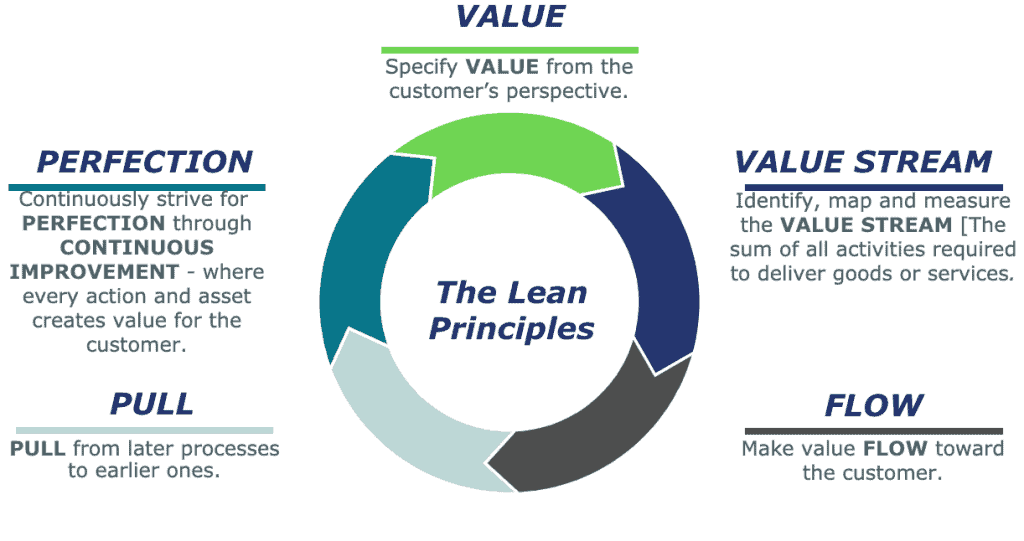
Lean’s core elements help organizations achieve operational excellence. Let’s break them down: What is lean
Value streams:
Identify and optimize the series of processes that create value for your customers. Think of it like a river, flowing smoothly from start to finish.
Example: A food manufacturer like General Mills streamlines their value stream to ensure a smooth flow from raw materials to finished goods, resulting in fresher products for consumers. What is lean
Continuous flow:
Eliminate interruptions and bottlenecks to create a seamless workflow.
Example: A hospital like the Cleveland Clinic implemented continuous flow in their surgical suites, reducing turnaround time between surgeries by 50% and increasing patient satisfaction. What is lean
Pull production:
Produce only what’s needed, when it’s needed, to avoid waste and overproduction.
Example: A tech company like Dell uses pull production to build computers to order, reducing inventory waste and allowing for greater customization. What is lean
Perfection:
Strive for flawless execution and continuous improvement.
Example: A world-class airline like Singapore Airlines constantly seeks perfection in its service, resulting in industry-leading customer satisfaction ratings. What is lean
These elements work together like a symphony, creating a culture of efficiency, effectiveness, and continuous improvement. By embracing these principles, organizations can achieve remarkable results and delight their customers.
Identifying and eradicating non-value-added activities

The Lean journey begins with a critical step: identifying and eliminating waste. Waste is any activity that doesn’t add value to your product, service, or customer. It’s the enemy of efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. What is lean
The 8 types of waste
Lean identifies 8 types of waste, known as the “8 deadly wastes”:
- Transportation waste: Moving materials or products unnecessarily.
- Inventory waste: Excess materials or products that need to be used.
- Motion waste: Unnecessary movement or action.
- Waiting for waste: Idle time due to equipment or process downtime.
- Overproduction waste: Producing more than what’s needed.
- Overprocessing waste: Using more resources or effort than necessary.
- Defect waste: Errors or defects that require rework.
- Skills waste: Underutilizing employees’ skills and abilities.
Real-life examples
A manufacturer like Nike reduced transportation waste by implementing a just-in-time inventory system, saving millions of dollars.
A hospital like the Mayo Clinic eliminated waiting waste by streamlining patient flow, reducing wait times by 50%.
Software companies like Microsoft reduced defect waste by implementing automated testing, resulting in fewer bugs and happier customers. What is lean
The human impact
Eliminating waste isn’t just about efficiency; it’s also about people. By reducing waste, organizations can:
- Free up employees’ time to focus on value-added activities
- Improve job satisfaction and engagement
- Enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Increase productivity and profitability
Organizations can unlock their full potential and achieve remarkable results by identifying and eradicating non-value-added activities.
Encouraging staff to drive continuous improvement
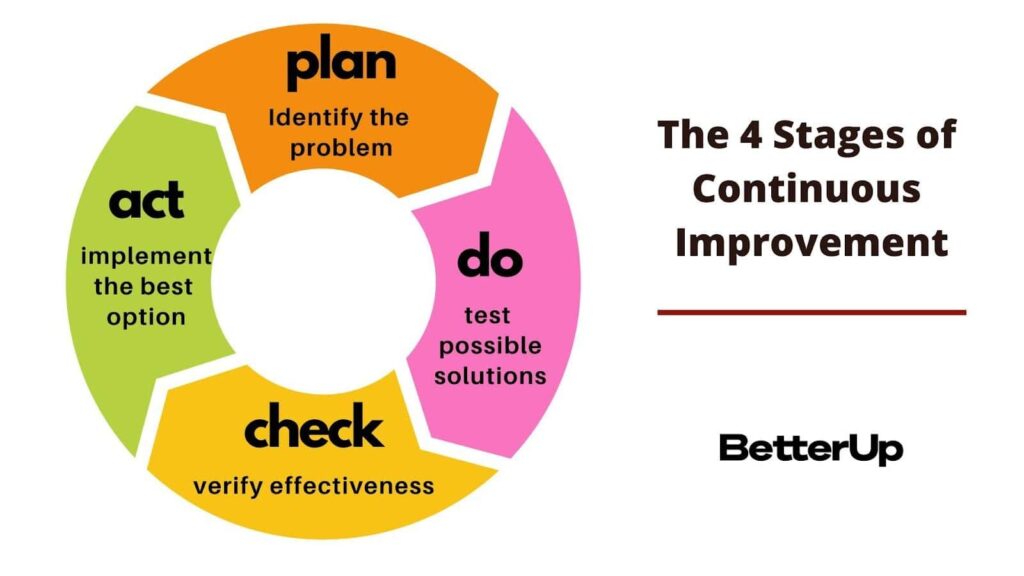
Continuous improvement is a core principle of Lean, and it relies on the active involvement of all staff members. When employees are empowered to identify areas for improvement and implement changes, they become engaged, motivated, and invested in the organization’s success. What is lean
Empowering employees
Encouraging staff to drive continuous improvement requires a culture shift. It means:
- Trusting employees to take ownership of their work and make decisions.
- Providing training and resources to equip them with the skills and knowledge they need
- Encouraging experimentation and learning from failures.
Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions.
Real-life examples
- Toyota’s suggestion system: Employees submit over 1 million suggestions annually, resulting in significant cost savings and efficiency gains.
- Google’s 20% time: Employees dedicate 20% of their work time to side projects, leading to innovations like Gmail and Google Maps.
The Cleveland Clinic’s ” Idea of the Week”: Employees submit ideas for improvement, resulting in over 1,000 implemented changes annually.
The human impact
When employees are encouraged to drive continuous improvement, they:
- Feel valued and respected for their contributions
- Develop a sense of pride and ownership in their work
- Grow professionally and develop new skills
- Improve job satisfaction and engagement
By empowering employees to drive continuous improvement, organizations can tap into their collective creativity, enthusiasm, and expertise, leading to remarkable results and a competitive edge. What is lean
Streamlining workflows for efficiency and effectiveness
Lean is all about optimizing workflows to achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness. By streamlining processes, organizations can reduce waste, improve quality, and increase productivity. What is lean
Simplifying and standardizing
Streamlining workflows involves:
- Simplifying processes by eliminating unnecessary steps
- Standardizing tasks to ensure consistency and quality
- Visualizing workflows to identify areas for improvement
- Continuously improving processes based on feedback and data
Real-life examples
- Amazon’s Fulfillment Centers: Streamlined workflows enable fast and efficient order processing, with some centers shipping over 1 million packages per day!
- The Mayo Clinic’s Patient Flow: Standardized workflows ensure patients receive timely and high-quality care, resulting in improved patient satisfaction and outcomes.
- Toyota’s Production Line: Simplified and standardized workflows enable the production of high-quality vehicles at an impressive pace.
The human impact
Streamlining workflows has a significant impact on employees and customers:
- Reduced frustration and stress for employees
- Improved job satisfaction and engagement
- Enhanced customer experience and loyalty
- Increased productivity and efficiency
By streamlining workflows, organizations can achieve remarkable results, improve employee morale, and delight their customers.
Tracking lead time, throughput, defect rate, and more

To achieve operational excellence, organizations need to measure and track key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics provide valuable insights into process efficiency, effectiveness, and quality. What is lean
Key metrics
Some essential KPIs in Lean include:
- Lead time: Time from order to delivery
- Throughput: Quantity produced within a given time
- Defect rate: Number of defects per unit
- First-pass yield: Percentage of defect-free products
- Cycle time: Time to complete a process or task
Inventory turnover: Ratio of sales to inventory
Real-life examples
Amazon’s Fulfillment Centers: Track lead time, throughput, and inventory turnover to ensure fast and efficient order processing.
The Cleveland Clinic’s Surgery Department: Monitor lead time, cycle time, and defect rate to optimize surgical procedures and patient care.
Toyota’s Manufacturing Plants: Track first-pass yield, defect rate, and inventory turnover to ensure high-quality vehicles and efficient production.
The human impact
Tracking KPIs has a significant impact on employees and customers:
- Improved transparency and accountability
- Data-driven decision-making
- Employee engagement and motivation
- Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Continuous improvement and innovation
By tracking and analyzing KPIs, organizations can identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and achieve remarkable results. What is lean
Starting small, building a team, and providing training

Implementing Lean principles requires a thoughtful and incremental approach. It’s essential to start small, build a dedicated team, and provide comprehensive training to ensure a successful transformation. What is lean
Start small
- Pilot projects: Begin with a limited scope to test and refine Lean principles
- Quick wins: Achieve early successes to build momentum and confidence
- Lessons learned: Apply insights from pilot projects to broader implementation
Build a team
- Cross-functional: Assemble a team with diverse skills and perspectives
- Empowerment: Give team members autonomy to make decisions and drive change
- Collaboration: Foster open communication and teamwork
Provide training
- Lean principles: Educate team members on core concepts and tools
- Workshop and coaching: Offer hands-on training and guidance
- Continuous learning: Encourage ongoing development and improvement
Real-life examples
GE Healthcare: Started small with pilot projects, then scaled up Lean implementation across the organization.
The Cleveland Clinic: Built a dedicated team to drive Lean transformation, resulting in significant improvements in patient care and efficiency.
Toyota: Provided comprehensive training to employees, enabling them to apply Lean principles and tools to achieve world-class quality and efficiency.
The human impact
Starting small, building a team, and providing training has a profound impact on employees and organizations:
- Builds confidence and trust
- Fosters collaboration and teamwork
- Develops new skills and expertise
- Drives engagement and motivation
- Sustains continuous improvement
Improved quality, reduced costs, increased productivity, and enhanced customer satisfaction

The benefits of Lean implementation are numerous and far-reaching, impacting various aspects of an organization’s performance.
Improved quality
Defect reduction: Fewer errors and mistakes
Consistency: Standardized processes ensure uniform quality
Reliability: Improved performance and durability
Reduced costs
- Efficiency gains: Streamlined processes reduce waste and labor
- Inventory reduction: Just-in-time production minimizes excess inventory
- Extended equipment life: Regular maintenance reduces replacement costs
Increased productivity
- Faster throughput: Improved processes speed up production
- Increased capacity: Existing resources can handle more work
- Better resource allocation: Optimal use of skills and talent
Enhanced customer satisfaction
- Faster delivery: Reduced lead times meet customer needs sooner
- Improved responsiveness: Quick resolution of customer complaints
- Higher quality products: Meets or exceeds customer expectations
Real-life examples
Toyota: Improved quality and reduced costs enabled the company to pass savings on to customers, increasing market share.
Amazon: Increased productivity and faster delivery times have led to unparalleled customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The Cleveland Clinic: Improved quality and reduced costs have resulted in better patient outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
The human impact
Lean implementation has a profound impact on employees and customers:
- Increased pride in workmanship and quality
- Improved job satisfaction through empowerment and engagement
- Enhanced customer loyalty and trust
- Better patient outcomes and improved healthcare experiences
- Increased competitiveness and market leadership
Addressing cultural resistance, leadership commitment, and sustainability

Implementing Lean principles requires more than just technical expertise; it demands a cultural transformation. Organizations must address cultural resistance, secure leadership commitment, and prioritize sustainability to ensure a successful and lasting transformation.
Addressing cultural resistance
- Communicate the why: Explain the purpose and benefits of Lean to all stakeholders
- Involve employees: Engage employees in the transformation process
- Address fears and concerns: Provide support and training to alleviate anxiety
Leadership commitment
- Lead by example: Leaders must model Lean behaviors and principles
- Provide resources: Allocate necessary resources and support for Lean initiatives
- Set clear expectations: Establish clear goals and metrics for Lean transformation
Sustainability
- Continuous improvement: Encourage ongoing learning and improvement
- Monitor progress: Track key performance indicators and adjust course as needed
- Celebrate successes: Recognize and celebrate Lean achievements
Real-life examples
General Electric: Addressed cultural resistance by engaging employees in Lean training and development.
The Cleveland Clinic: Secured leadership commitment by setting clear goals and expectations for Lean transformation.
Toyota: Prioritized sustainability by continuously improving processes and encouraging employee innovation.
The human impact
Addressing cultural resistance, leadership commitment, and sustainability has a profound impact on employees and organizations:
- Builds trust and engagement
- Fosters a culture of continuous improvement
- Develops leaders and empowers employees
- Drives long-term success and sustainability
- Enhances reputation and attracts top talent
Embedding Lean into your organization's culture and continuously improving

The ultimate goal of Lean is to create a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are empowered to identify and solve problems. By embedding Lean into your organization’s culture, you can ensure a sustainable and lasting transformation.
Make Lean a way of life
- Integrate Lean into daily work: Encourage employees to apply Lean principles in their daily tasks
- Recognize and reward Lean behavior: Celebrate employees who demonstrate Lean thinking and behavior
- Provide ongoing training and development: Offer regular training and coaching to deepen Lean knowledge and skills
Continuous improvement
- Encourage experimentation: Allow employees to try new approaches and learn from failures
- Foster a culture of feedback: Encourage open and constructive feedback to drive improvement
- Set goals and metrics: Establish clear targets and metrics to measure progress and drive continuous improvement
Real-life examples
- Toyota: Embedded Lean into its culture by making it a core part of its values and principles.
- Amazon: Encourages continuous improvement by giving employees the autonomy to experiment and innovate.
- The Cleveland Clinic: Made Lean a way of life by integrating it into daily work and recognizing and rewarding Lean behavior.
The human impact
Embedding Lean into your organization’s culture and continuously improving has a profound impact on employees and organizations:
- Empower employees to take ownership and drive improvement
- Fosters a culture of innovation and experimentation
- Drives engagement and motivation
- Enhances reputation and attracts top talent
- Sustains long-term success and competitiveness

