Imagine a world where the skies are filled with buzzing drones, each performing a unique task. These unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) are revolutionizing various industries, from delivering packages to monitoring crops. But what exactly are UAS, and what makes them tick? In this article, we’ll explore the definiti on and basic components of UAS, unraveling the technology behind these fascinating machines. Stay with us as we dive into the world of drones and discover how they are shaping our future. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Categories Based on Size, Range, and Capabilities
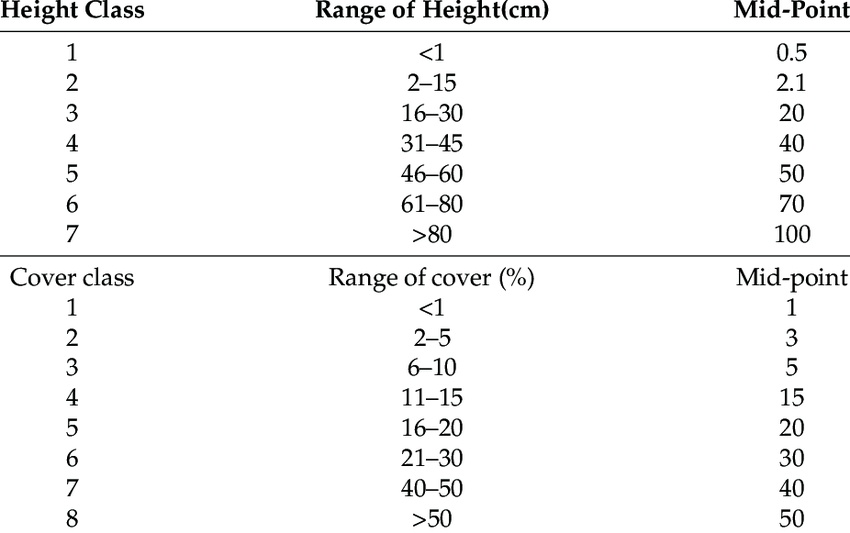
Drones come in all shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks and environments. Understanding these categories helps us appreciate the versatility and innovation behind unmanned aircraft systems (UAS).
Size Categories
1. Nano Drones
- Description: Tiny, lightweight drones that can fit in the palm of your hand.
- Example: The DJI Tello, is popular among hobbyists and educators for its ease of use and affordability.
- Human Touch: Imagine a child flying a nano drone in their backyard, learning the basics of aerodynamics and having fun.
2. Micro Drones
- Description: Slightly larger than nano drones, often used for indoor applications.
- Example: The Parrot Mambo, known for its stability and ability to perform tricks.
- Human Touch: Picture a family gathering where a micro drone captures candid moments, adding a unique perspective to cherished memories.
3. Small Drones
- Description: Commonly used for recreational and commercial purposes, offering a balance between size and functionality.
- Example: The DJI Mavic Air, is favored by photographers and videographers for its high-quality camera and portability.
- Human Touch: Envision a travel blogger using a small drone to capture breathtaking aerial shots of a remote island, sharing the beauty of the world with their followers.
4. Medium Drones
- Description: Larger drones with enhanced capabilities, are often used in professional settings.
- Example: The DJI Matrice 300, utilized in industrial inspections and search and rescue missions.
- Human Touch: Think of a team of engineers using a medium drone to inspect a wind turbine, ensuring its safety and efficiency without risking human lives.
5. Large Drones
- Description: Heavy-duty drones are designed for specialized tasks, such as cargo delivery and military operations.
- Example: The MQ-9 Reaper, used by the military for surveillance and reconnaissance.
- Human Touch: Imagine a large drone delivering medical supplies to a remote village, providing essential aid in times of crisis.
Range Categories
1. Short-Range Drones
- Description: Designed for proximity tasks, typically within a few kilometers.
- Example: The DJI Spark, ideal for quick, spontaneous flights.
- Human Touch: Picture a group of friends at a park, using a short-range drone to capture their picnic from above, creating lasting memories.
2. Medium-Range Drones
- Description: Capable of covering moderate distances, often used in agriculture and surveying.
- Example: The DJI Phantom 4, known for its reliability and precision.
- Human Touch: Envision a farmer using a medium-range drone to monitor crop health, ensuring a bountiful harvest and supporting their livelihood.
3. Long-Range Drones
- Description: Built for extended missions, capable of traveling hundreds of kilometers.
- Example: The Global Hawk, used for long-duration surveillance and data collection.
- Human Touch: Imagine scientists using a long-range drone to study wildlife in remote areas, gathering crucial data to protect endangered species.
Capability Categories
1. Reconnaissance Drones
- Description: Equipped with advanced sensors and cameras for surveillance and data collection.
- Example: The RQ-4 Global Hawk, providing real-time intelligence for military operations.Human Touch: Think of a wildlife conservationist using a reconnaissance drone to track animal movements, aiding in the preservation of natural habitats. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
2. Delivery Drones
- Description: Designed to transport goods, ranging from small packages to larger cargo.
- Example: The Amazon Prime Air drone, aimed at revolutionizing the delivery industry.
- Human Touch: Picture a delivery drone bringing essential supplies to a disaster-stricken area, offering hope and relief to those in need.
3. Agricultural Drones
- Description: Specialized for farming tasks, such as crop monitoring and spraying.
- Example: The DJI Agras, enhancing agricultural productivity and efficiency.Human Touch: Envision a farmer using an agricultural drone to optimize irrigation, ensuring sustainable farming practices and a better future for their community. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Key Technologies: Sensors, Cameras, GPS, and AI
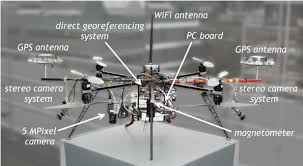
The magic behind unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) lies in the advanced technologies that power them. Let’s delve into the key components that make drones so versatile and effective. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Sensors
Description: Sensors are the eyes and ears of a drone, providing crucial data about the environment.
Example: LIDAR sensors, which use laser light to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps.
Human Touch: Imagine a rescue team using a drone equipped with LIDAR sensors to navigate through a collapsed building, locating survivors quickly and safely.
Cameras
Description: Cameras capture high-resolution images and videos, enabling a wide range of applications from filmmaking to surveillance.
Example: The DJI Zenmuse X7, a professional-grade camera used in aerial cinematography.
Human Touch: Picture a filmmaker using a drone with a high-quality camera to shoot a breathtaking aerial scene for a documentary, bringing viewers closer to nature’s wonders.
GPS
Description: GPS technology allows drones to navigate accurately and maintain stable flight paths.
Example: The GPS module in the DJI Phantom series, ensures precise positioning and autonomous flight capabilities.
Human Touch: Envision a farmer using a GPS-enabled drone to map their fields, optimizing planting patterns and improving crop yields, ultimately supporting their family’s livelihood.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Description: AI enhances a drone’s ability to process data, make decisions, and perform complex tasks autonomously.
Example: The Skydio 2, which uses AI for obstacle avoidance and autonomous flight.
Human Touch: Think of a wildlife researcher deploying an AI-powered drone to track animal movements in dense forests, gathering valuable data without disturbing the natural habitat. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Military and Defense Applications

Drones have revolutionized modern warfare, offering unparalleled capabilities in surveillance, reconnaissance, and combat. Let’s explore some key military applications of drones, highlighting real-life examples and their impact on human lives. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Surveillance and Reconnaissance
Description: Drones equipped with advanced sensors and cameras provide real-time intelligence, crucial for military operations.
Human Touch: Imagine a soldier stationed at a remote outpost, relying on drone footage to monitor enemy movements and ensure the safety of their comrades. The drone’s eyes in the sky offer a sense of security and strategic advantage. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Combat and Strike Missions
Description: Armed drones can carry out precision strikes, minimizing the risk to human soldiers.
Example: The MQ-9 Reaper, used by the U.S. military, is known for its precision targeting capabilities.
Human Touch: Picture a military commander using a drone to neutralize a high-value target, preventing potential threats to civilian lives and reducing the need for ground troops in dangerous areas. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Search and Rescue Operations
Description: Drones can quickly locate and assist in the rescue of injured or trapped personnel in hostile environments.
Human Touch: Envision a drone locating a wounded soldier in a war zone, guiding medics to the exact location, and saving precious time. The drone’s swift response can mean the difference between life and death. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Electronic Warfare
Description: Drones can be equipped with electronic warfare systems to disrupt enemy communications and radar.
Human Touch: Think of a drone jamming enemy communications, allowing friendly forces to move undetected and carry out their mission safely. The drone’s role in electronic warfare helps protect soldiers on the ground. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Logistics and Supply Delivery
Description: Drones can transport supplies and equipment to troops in remote or dangerous areas.
Example: The U.S. military has experimented with using drones for delivering medical supplies to frontline units.
Human Touch: Imagine a drone delivering essential medical supplies to a field hospital in a conflict zone, ensuring that injured soldiers receive timely care. The drone’s ability to navigate through hostile territory brings hope and relief to those in need.
Overview of Global and Local Regulations

Navigating the complex landscape of global and local regulations is crucial for businesses and governments alike. Regulations are designed to ensure safety, fairness, and sustainability, but they can vary significantly from one region to another. Understanding these differences and how they impact operations is essential for compliance and success.
Global Regulations
Global regulations often aim to create a standardized framework that can be applied across multiple countries. These regulations are typically established by international organizations or agreements between countries. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union sets a high standard for data privacy and protection, influencing data handling practices worldwide.
Another example is the Paris Agreement, an international treaty on climate change. Countries that are part of this agreement commit to reducing their greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate global warming. This has led to various national policies aimed at promoting renewable energy and reducing carbon footprints. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Local Regulations
Local regulations, on the other hand, are specific to individual countries or regions. These regulations address local needs and priorities, which can differ widely. For instance, in the United States, the Clean Air Act regulates air emissions from stationary and mobile sources to ensure air quality. Meanwhile, in India, the Plastic Waste Management Rules aim to reduce plastic waste and promote recycling. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
In Pakistan, the Punjab Environmental Protection Act focuses on controlling pollution and protecting the environment within the province of Punjab. This includes regulations on industrial emissions, waste management, and water quality. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Real-Life Examples
To illustrate the impact of these regulations, let’s look at some real-life examples:
1. GDPR Compliance in Tech Companies: When the GDPR was implemented, tech giants like Google and Facebook had to overhaul their data privacy policies. This included providing users with more control over their data and ensuring transparent data processing practices. The regulation not only affected companies in the EU but also those outside the EU that handle EU citizens’ data. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
2. Renewable Energy in India: Under the Paris Agreement, India has made significant strides in expanding its renewable energy capacity. The country has invested heavily in solar power, with projects like the Kamuthi Solar Power Project in Tamil Nadu, which is one of the largest solar power plants in the world. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
3. Plastic Ban in Kenya: Kenya implemented one of the world’s strictest plastic bag bans in 2017. The ban has significantly reduced plastic waste in the environment, although it has also posed challenges for businesses that rely on plastic packaging. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Human Touch
Regulations, while sometimes seen as bureaucratic hurdles, play a vital role in protecting our health, environment, and rights. They ensure that businesses operate fairly and sustainably, benefiting society as a whole. For instance, the reduction in plastic waste in Kenya not only helps the environment but also improves the quality of life for its citizens by reducing pollution. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Similarly, the push for renewable energy in India not only addresses climate change but also creates jobs and promotes energy security. These regulations reflect our collective efforts to create a better, more sustainable world for future generations. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Current Challenges: Privacy, Security, and Airspace Integration
As the use of Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), commonly known as drones, continues to expand, several challenges have emerged. These challenges primarily revolve around privacy, security, and the integration of drones into existing airspace systems. Addressing these issues is crucial for the safe and effective use of drones in various sectors. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Privacy
Privacy concerns are paramount when it comes to drone operations. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can capture detailed images and data, potentially infringing on individuals’ privacy. For instance, there have been instances where drones have been used to capture unauthorized footage of private properties, leading to legal disputes and public outcry.
Real-Life Example: In 2014, a man in Kentucky shot down a drone that was flying over his property, claiming it was an invasion of his privacy. This incident highlighted the tension between drone operators and individuals concerned about their privacy rights. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Security
Security is another significant challenge. Drones can be used for malicious purposes, such as smuggling contraband into prisons or conducting surveillance for criminal activities. Ensuring that drones are not used for such purposes requires robust security measures and regulations. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Real-Life Example: In 2015, a drone carrying drugs, a cell phone, and a weapon crashed into a prison yard in Ohio, USA. This incident underscored the need for stringent security protocols to prevent the misuse of drones. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Airspace Integration
Integrating drones into the national airspace system is a complex task. It involves ensuring that drones can safely coexist with manned aircraft without causing disruptions or accidents. This requires advanced traffic management systems and clear regulations. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Real-Life Example: The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States has been working on the Low Altitude Authorization and Notification Capability (LAANC) system. This system allows drone operators to obtain real-time authorization to fly in controlled airspace, ensuring safe and efficient airspace integration. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Human Touch
These challenges are not just technical or regulatory issues; they have real impacts on people’s lives. Privacy concerns can lead to a sense of intrusion and loss of personal space. Security breaches can cause fear and mistrust. Effective airspace integration can prevent accidents and ensure the safety of both drone operators and the general public. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between governments, industry stakeholders, and the public. By working together, we can harness the benefits of drone technology while mitigating its risks. It’s about finding a balance that respects privacy, ensures security, and integrates new technology seamlessly into our daily lives. Unmanned Aircraft System Drone

