In the digital age, the terms “cybersecurity” and “cyber security” often pop up, but do they mean the same thing? While they might seem interchangeable, subtle differences exist. This article dives into these distinctions, exploring regional preferences and usage trends. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a curious reader, understanding these nuances can enhance your grasp of the digital world. Keep reading to uncover the fascinating details behind these terms! Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
A Brief History of the Term’s Evolution and Adoption
The journey of the term “cybersecurity” (or “cyber security”) is as dynamic as the digital landscape it describes. Initially, the concept emerged in the late 20th century, when the internet began to expand beyond academic and military use. Early on, the focus was on securing computer systems and networks from unauthorized access and data breaches. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
In the United States, the term “cybersecurity” became more prevalent, reflecting a holistic approach to protecting digital infrastructure. Meanwhile, in the United Kingdom and other parts of the world, “cyber security” was often used, emphasizing the security aspect of cyberspace. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Real-Life Examples and Human Touch
Consider the infamous Morris Worm incident of 1988, one of the first major cyberattacks. This event highlighted the need for robust cybersecurity measures and led to increased awareness and development in the field. Fast forward to the 2010s, the Stuxnet worm targeted industrial systems, showcasing the global implications of cyber threats and the necessity for international cooperation in cybersecurity.
In industries, the financial sector was among the first to adopt stringent cybersecurity practices, driven by the need to protect sensitive customer data. Today, sectors like healthcare and energy are also heavily investing in cybersecurity to safeguard critical infrastructure and personal information. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
On a personal level, think about how often we hear about data breaches affecting millions of users. These incidents remind us of the importance of cybersecurity in our daily lives, from protecting our social media accounts to ensuring the safety of our online transactions.
The Crucial Role of Cybersecurity in Today’s Digital Age

In our increasingly digital world, cybersecurity has become a cornerstone of modern life. With the proliferation of internet-connected devices and the vast amounts of data generated daily, the need to protect our digital assets has never been more critical. Cyber threats and attacks are on the rise, targeting individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Real-Life Examples and Human Touch
Consider the WannaCry ransomware attack of 2017, which affected over 200,000 computers across 150 countries. This attack crippled hospitals, businesses, and government agencies, demanding ransom payments to unlock encrypted data. The widespread impact of WannaCry underscored the vulnerability of our digital infrastructure and the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures.
On a more personal level, think about the countless phishing emails we receive, attempting to steal our personal information. For instance, a friend of mine recently fell victim to a phishing scam, losing access to their bank account and personal data. This incident was a stark reminder of how easily cyber threats can infiltrate our lives and the importance of staying vigilant.
Businesses are also prime targets for cyberattacks. The Equifax data breach in 2017 exposed the personal information of 147 million people, including Social Security numbers and credit card details. This breach not only caused significant financial loss but also eroded public trust in the company’s ability to safeguard sensitive information.
The Growing Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, with attackers employing increasingly sophisticated techniques. From malware and ransomware to phishing and denial-of-service attacks, the methods used to compromise systems are diverse and constantly changing. This dynamic threat landscape requires continuous adaptation and improvement of cybersecurity practices.
The Human Element
At the heart of cybersecurity is the human element. It’s not just about technology; it’s about people. Educating individuals about safe online practices, fostering a culture of security within organizations, and encouraging collaboration between governments and private sectors are all essential components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Key Elements of Effective Cybersecurity Measures

In today’s interconnected world, safeguarding our digital assets requires a multi-layered approach. Here are some of the main elements that constitute effective cybersecurity measures: Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Firewalls
Firewalls act as the first line of defense, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. They create a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, such as the Internet. For example, a company might use a firewall to block unauthorized access to its internal servers, ensuring that only legitimate traffic is allowed through. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. It ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the decryption key. A real-life example is the use of encryption in online banking. When you log into your bank account, your data is encrypted to protect your personal and financial information from cybercriminals. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a system. This could include something you know (like a password), something you have (like a smartphone), or something you are (like a fingerprint). For instance, many email services now offer MFA, where you need to enter a code sent to your phone in addition to your password. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Real-Life Examples and Human Touch
Consider the case of a small business owner who implemented MFA after a phishing attack compromised their email account. By adding this extra layer of security, they significantly reduced the risk of future breaches. Similarly, a friend of mine recently started using a password manager that encrypts all their passwords, making it much harder for hackers to gain access to their accounts.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and potential threats. They can detect and respond to intrusions in real time, helping to prevent data breaches. For example, an IDPS might alert a company to unusual login attempts from different geographic locations, allowing them to take immediate action. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Regular Updates and Patches
Keeping software and systems up to date is crucial for cybersecurity. Regular updates and patches fix vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit. A well-known example is the WannaCry ransomware attack, which exploited a vulnerability in outdated Windows systems. Organizations that had applied the necessary patches were protected from the attack. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
User Awareness and Training
Human error is often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Educating users about safe online practices, such as recognizing phishing emails and using strong passwords, is essential. For instance, a company might conduct regular training sessions to ensure employees are aware of the latest cyber threats and how to avoid them. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Explore How New Technologies Like AI and IoT Are Impacting Cybersecurity, Both Positively and Negatively

The rapid advancement of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) has brought about significant changes in the field of cybersecurity. These technologies offer both promising solutions and new challenges. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Positive Impacts
1. Enhanced Threat Detection and Response: AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyber threat. For instance, AI-driven security systems can detect unusual login attempts or data transfers, flagging potential breaches before they cause significant damage. This proactive approach helps organizations respond to threats more swiftly and effectively. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
2. Automated Security Measures: AI can automate routine security tasks, such as software updates and patch management, reducing the burden on IT teams and minimizing human error. This automation ensures that systems are always up-to-date with the latest security measures, making it harder for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
3. Improved User Authentication: IoT devices often come with biometric authentication features, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, which enhance security by making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access. These advanced authentication methods are more secure than traditional passwords, which can be easily compromised. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Negative Impacts
1. Increased Attack Surface: The proliferation of IoT devices means more entry points for cyber attackers. Each connected device, from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, can potentially be exploited if not properly secured. For example, a hacker could gain access to a smart thermostat and use it as a gateway to infiltrate a home network. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
2. Sophisticated AI-Driven Attacks: Just as AI can be used to defend against cyber threats, it can also be weaponized by attackers. AI can create more sophisticated phishing attacks that are harder to detect. For instance, AI-generated deepfake videos or voice messages can be used to impersonate trusted individuals, tricking victims into divulging sensitive information. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
3. Data Privacy Concerns: IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, often including personal information. If these devices are compromised, the data they hold can be exposed, leading to privacy breaches. For example, a compromised smart home device could reveal details about a person’s daily routines and habits. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Real-Life Examples
Positive Example: IBM’s Watson for Cyber Security uses AI to analyze and interpret vast amounts of security data, helping organizations identify and respond to threats more quickly. This system has been instrumental in reducing the time it takes to detect and mitigate cyber threats. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Negative Example: In 2016, the Mirai botnet attack exploited IoT devices like cameras and routers to launch a massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, disrupting major websites and services across the internet. This incident highlighted the vulnerabilities of IoT devices and the potential scale of attacks they can facilitate. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Human Touch
Imagine a small business owner, Sarah, who recently adopted smart security cameras to monitor her store. These cameras, connected to the internet, provide her with peace of mind as she can check on her store remotely. However, Sarah is also aware of the potential risks. She ensures her devices are regularly updated and uses strong, unique passwords to protect them. Sarah’s story illustrates the balance between leveraging new technologies for convenience and being vigilant about cybersecurity.
Summarize the Current Regulations and Compliance Requirements Related to Cybersecurity, and How They Differ Globally

Cybersecurity regulations and compliance requirements vary significantly across different regions, reflecting diverse legal frameworks, cultural attitudes, and levels of technological advancement. Here’s an overview of some key regulations and how they differ globally. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
United States
European Union
The EU has a more unified approach to cybersecurity, primarily through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
GDPR: Enforces strict data protection and privacy rules for all companies operating within the EU or handling EU citizens’ data. It includes requirements for data breach notifications, data protection officers, and hefty fines for non-compliance. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Asia-Pacific
Countries in the Asia-Pacific region have diverse approaches to cybersecurity:
Real-Life Example
Positive Example: A U.S. healthcare provider, aware of HIPAA requirements, implemented robust encryption and access controls to protect patient data. This proactive approach not only ensured compliance but also built trust with patients, knowing their sensitive information was secure.
Negative Example: In 2018, British Airways faced a significant GDPR fine after a data breach exposed the personal information of over 400,000 customers. This incident underscored the importance of stringent cybersecurity measures and compliance with data protection regulations.
Human Touch
Consider Maria, a small business owner in Spain. She runs an online store and recently expanded her customer base to include clients from across the EU. To comply with GDPR, Maria invested in a comprehensive data protection strategy, including customer consent forms and regular security audits. While this required time and resources, Maria feels confident that her business is now better protected against cyber threats, and her customers appreciate the transparency and commitment to their privacy.
Best Practices for Organizations: Provide Actionable Tips and Strategies for Businesses to Enhance Their Cybersecurity Posture, Including Employee Training and Incident Response Planning
In today’s digital age, enhancing cybersecurity is essential for businesses of all sizes. Here are some actionable tips and strategies to help organizations strengthen their cybersecurity posture. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
1. Conduct Regular Employee Training
Why It Matters: Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Regular training ensures they are aware of the latest threats and know how to respond appropriately. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Actionable Tips:
Phishing Simulations: Conduct regular phishing simulations to educate employees on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts.
Security Awareness Programs: Implement ongoing security awareness programs that cover topics like password management, safe browsing habits, and recognizing social engineering attacks.
Real-Life Example: A mid-sized company in the finance sector reduced successful phishing attacks by 70% after implementing quarterly phishing simulations and security awareness training sessions.
2. Develop a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
Why It Matters: An effective incident response plan helps organizations quickly and efficiently handle security breaches, minimizing damage and recovery time. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Actionable Tips:
Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly outline the roles and responsibilities of each team member involved in incident response.
Regular Drills: Conduct regular incident response drills to ensure all team members are familiar with the procedures and can act swiftly in the event of a breach.
Post-Incident Analysis: After an incident, conduct a thorough analysis to identify what went wrong and how to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Real-Life Example: A tech startup successfully mitigated a ransomware attack by following their well-rehearsed incident response plan, which included immediate isolation of affected systems and communication with stakeholders. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Why It Matters: MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
Actionable Tips:
Use MFA for All Critical Systems: Ensure that all critical systems and applications require MFA for access.
Educate Employees: Train employees on the importance of MFA and how to use it effectively.
Real-Life Example: A healthcare provider significantly reduced unauthorized access incidents by implementing MFA across all their systems, protecting sensitive patient data.
4. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Why It Matters: Keeping systems and software up-to-date helps protect against known vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Actionable Tips:
Automate Updates: Use automated tools to ensure that all systems and software are regularly updated and patched.
Patch Management Policy: Develop and enforce a patch management policy that prioritizes critical updates.
Real-Life Example: A retail company avoided a major data breach by promptly applying a critical security patch to their point-of-sale systems, which had been identified as vulnerable.
5. Monitor and Analyze Network Traffic
Why It Matters: Continuous monitoring helps detect unusual activity that could indicate a security breach.
Actionable Tips:
Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implement IDS to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular network audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Real-Life Example: A manufacturing firm detected and thwarted a cyber attack by using an IDS that flagged unusual data transfers, allowing them to take immediate action. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
Human Touch
Imagine a small business owner, Ahmed, who runs an online retail store. Ahmed recently attended a cybersecurity workshop and realized the importance of protecting his business from cyber threats. He decided to implement MFA, conduct regular employee training, and develop an incident response plan. Although these measures required an initial investment of time and resources, Ahmed now feels more confident that his business is better protected against cyber threats. His employees also appreciate the training, as it empowers them to contribute to the company’s security.
Predict Future Trends in Cybersecurity, Considering Technological Advancements and Evolving Threats
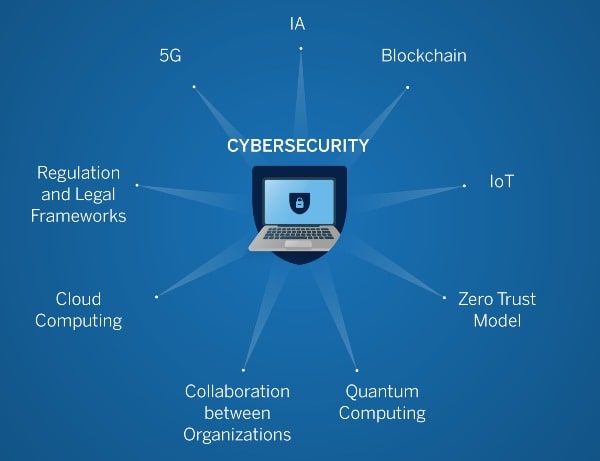
As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods and sophistication of cyber threats. Here are some key trends that are likely to shape the future of cybersecurity. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
1. Rise of AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
Trend: Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to launch more sophisticated attacks. AI can be used to automate phishing campaigns, create deepfake videos, and even develop malware that can adapt to evade detection.
Real-Life Example: In 2023, a major financial institution fell victim to an AI-driven phishing attack where deepfake audio was used to impersonate a senior executive, tricking employees into transferring funds to fraudulent accounts. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
2. Increased Focus on Zero Trust Architecture
Trend: The Zero Trust security model, which assumes that threats could be both external and internal, is gaining traction. This approach requires strict verification for anyone attempting to access resources within a network, regardless of their location.
Real-Life Example: A global tech company implemented a Zero Trust architecture, significantly reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access by continuously verifying user identities and device health. Cybersecurity or Cyber Security
3. Expansion of IoT Security Measures
Trend: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, securing these endpoints has become critical. Future cybersecurity strategies will focus on enhancing the security of IoT devices to prevent them from becoming entry points for attacks.
4. Growth of Cybersecurity Regulations
Trend: Governments worldwide are enacting stricter cybersecurity regulations to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure. These regulations will continue to evolve, requiring organizations to stay compliant with varying global standards.
Real-Life Example: The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has set a high standard for data protection, influencing other regions to adopt similar regulations. Companies operating globally must now navigate a complex landscape of compliance requirements.
5. Emphasis on Cyber Resilience
Trend: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations are focusing on building cyber resilience. This involves not only preventing attacks but also ensuring quick recovery and continuity of operations in the event of a breach.
Real-Life Example: A healthcare provider developed a robust cyber resilience plan that included regular backups, incident response drills, and collaboration with cybersecurity experts. This preparation enabled them to quickly recover from a ransomware attack with minimal disruption to patient care.
Human Touch
Consider the story of Raj, a small business owner who runs an online retail store. Raj recently attended a cybersecurity seminar and learned about the importance of staying ahead of evolving threats. He decided to implement a Zero Trust architecture, invest in AI-driven security tools, and regularly update his IoT devices. Although these measures required an initial investment, Raj now feels more confident that his business is better protected against cyber threats. His proactive approach not only safeguards his business but also builds trust with his customers, who appreciate the commitment to their data security.

