“Imagine a world where vaccines are ineffective, food is spoiled, and medicines are compromised. This is the reality without cold chain logistics. As a crucial part of the supply chain industry, cold chain logistics ensures the safe storage and transportation of temperature-sensitive goods. From life-saving medicines to fresh produce, this intricate network of refrigerated storage and transportation keeps our world healthy and thriving. In this article, we’ll delve into cold chain logistics, exploring its definition, importance, and impact on our daily lives. Let’s dive in!”
Key Components of Cold Chain Logistics
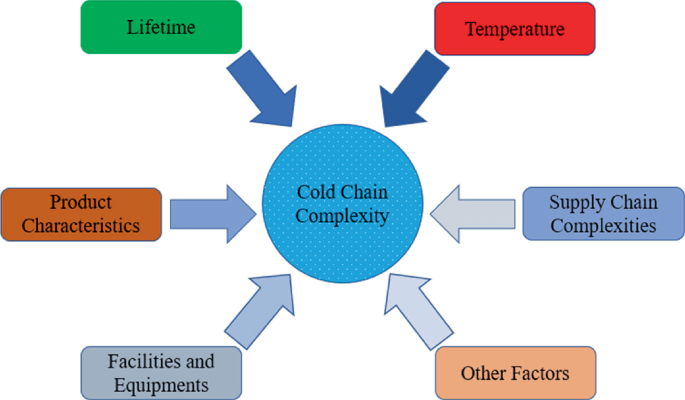
Cold chain logistics is a complex process involving multiple elements working harmoniously. Cold chain logistics comprises three essential components: temperature-controlled storage, transportation, and monitoring. Let’s break these down and explore real-life examples to illustrate their importance.
1. Temperature-Controlled Storage
Imagine a warehouse in Amsterdam storing vaccines for global distribution. The storage facility must maintain a consistent refrigerated temperature between 2-8°C (36-46°F) to ensure the vaccines’ potency. This is just one example of temperature-controlled storage, which is critical in cold chain logistics.
2. Transportation
Picture a refrigerated truck transporting perishable food items from a farm in California to a grocery store in New York. The truck’s temperature control system must maintain a consistent temperature throughout the journey to prevent spoilage. This is a classic example of cold chain transportation, where the right temperature is maintained during transit.
3. Monitoring
Consider a shipment of blood samples being transported from a hospital in London to a laboratory in Berlin. Real-time temperature monitoring ensures that the samples remain within the required temperature range (in this case, between 2-10°C or 36-50°F). This is where monitoring comes in – a crucial element that ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods throughout the supply chain.
These three elements – temperature-controlled storage, transportation, and monitoring – form the backbone of cold chain logistics. By understanding and implementing these components effectively, businesses can ensure the safe and efficient transportation of temperature-sensitive goods, ultimately saving lives and reducing waste.
Benefits of Cold Chain Logistics
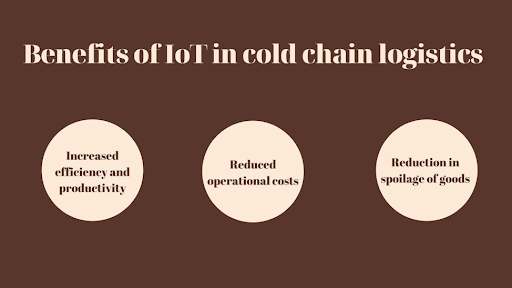
Cold chain logistics offers a multitude of advantages that impact businesses, consumers, and the environment. Let’s dive into the benefits and explore some real-life examples to illustrate the positive impact of cold chain logistics.
Reduced Spoilage
Imagine a grocery store in Mumbai receiving a shipment of fresh produce from a local farm. Thanks to cold chain logistics, the produce remains fresh, and the store can offer high-quality products to customers. A study by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) found that cold chain logistics can reduce food spoilage by up to 50%! This not only reduces food waste but also helps businesses save money.
Improved Product Quality
Consider a pharmaceutical company in the United States transporting life-saving vaccines to Africa. Cold chain logistics ensures that the vaccines remain effective and potent during transportation, resulting in improved product quality. This is critical in the pharmaceutical industry, where temperature excursions can compromise product integrity.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Picture a consumer in Tokyo ordering frozen pizza online and receiving it at their doorstep in perfect condition. Cold chain logistics makes this possible, ensuring that the pizza remains frozen and ready to eat. A survey by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) found that 70% of consumers are more likely to purchase perishable goods online if they are confident in the cold chain logistics process.
Additional Benefits
Cold chain logistics also offers other advantages, including:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements, such as those set by the FDA or EU GDP.
- Increased Shelf Life: Extending the shelf life of perishable products, reducing waste, and saving businesses money.
- Competitive Advantage: Differentiating businesses from competitors by offering high-quality, temperature-sensitive products.
By implementing effective cold chain logistics, businesses can reap these benefits, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction, reduced waste, and improved product quality.
Challenges in Cold Chain Logistics

While cold chain logistics offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that can impact businesses and consumers. Let’s explore some common obstacles and real-life examples to illustrate the complexities of cold chain logistics.
Maintaining Temperature Control
Imagine a refrigerated truck transporting vaccines from a manufacturer in Belgium to a hospital in Greece. The truck’s temperature control system fails, causing the vaccines to be exposed to temperatures above 8°C (46°F). This can lead to reduced potency or even spoilage, putting patient lives at risk. Temperature control is a critical challenge in cold chain logistics, requiring constant monitoring and maintenance.
Managing Costs
Consider a small pharmaceutical company in India trying to transport temperature-sensitive medicines to remote areas. The high cost of refrigerated transportation and storage can be a significant burden, making it difficult for the company to maintain profitability while ensuring product integrity. Managing costs is a delicate balancing act in cold chain logistics.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Picture a global logistics company transporting perishable goods across international borders. Ensuring compliance with diverse regulatory requirements, such as those set by the FDA, EU GDP, and WHO, can be a complex and time-consuming task. Non-compliance can result in fines, product recalls, or even legal action.
Additional Challenges
Other common obstacles in cold chain logistics include:
- Infrastructure Limitations: Inadequate infrastructure, such as a lack of refrigerated storage or transportation capacity, can hinder the cold chain process.
- Human Error: Mistakes made by personnel, such as incorrect temperature settings or inadequate monitoring, can compromise product integrity.
- Natural Disasters: Unforeseen events like natural disasters or power outages can disrupt the cold chain, putting products at risk.
By understanding these challenges, businesses and logistics providers can better prepare and implement strategies to mitigate risks, ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products and maintaining the trust of their customers.
Types of Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics encompasses a range of temperature-controlled transportation and storage solutions, each designed to meet specific product requirements. Let’s explore the different types of cold chain logistics and their real-life applications.
Refrigerated
Imagine a truck transporting fresh produce from a farm in California to a grocery store in New York. The truck’s refrigeration system maintains a consistent temperature between 2-8°C (36-46°F), ensuring the produce remains fresh and ready for consumption. This is an example of refrigerated cold chain logistics, commonly used for perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products.
Frozen
Picture a warehouse in Chicago storing frozen pizzas for a popular food chain. The warehouse maintains a temperature of -18°C (0°F), ensuring the pizzas remain frozen and ready for distribution. Frozen cold chain logistics is essential for products like meat, seafood, and frozen meals.
Cryogenic
Additional Types
Other types of cold chain logistics include:
- Chilled: Maintaining temperatures between 2-8°C (36-46°F) for products like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Deep Frozen: Storing products at temperatures below -30°C (-22°F) for long-term preservation, commonly used for biological samples and pharmaceuticals.
- Ultra-Low Temperature: Maintaining temperatures below -50°C (-58°F) for sensitive products like certain vaccines and biological materials.
Each type of cold chain logistics plays a critical role in ensuring the integrity and effectiveness of temperature-sensitive products, impacting various industries and ultimately, our daily lives.
Technology in Cold Chain Logistics
Technology plays a vital role in cold chain logistics, ensuring the integrity and safety of temperature-sensitive products. Let’s delve into the role of technology and explore real-life examples.
Temperature Monitoring Systems
Imagine a shipment of vaccines being transported from a manufacturer in the United States to a hospital in Africa. Temperature monitoring systems track the shipment’s temperature in real-time, sending alerts to logistics teams if there are any excursions outside the acceptable range. This ensures the vaccines’ potency and effectiveness.
Data Analytics
Picture a pharmaceutical company analyzing data on temperature excursions, transit times, and storage conditions to identify areas for improvement in their cold chain logistics. Data analytics helps optimize routes, reduce transit times, and improve temperature control, ultimately increasing product integrity.
IoT Solutions
Consider a refrigerated warehouse in Asia using IoT sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and storage conditions. IoT solutions provide real-time visibility, enabling logistics teams to respond quickly to any issues and ensuring the quality of stored products.
Additional Technologies
Other technologies used in cold chain logistics include:
- Blockchain: Ensuring transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain.
- Artificial Intelligence: Predicting potential disruptions and optimizing logistics operations.
- Robotics: Automating warehouse operations and reducing human error.
- Cloud Computing: Enabling real-time data access and collaboration across the supply chain.
Real-Life Examples
- UPS’s Temperature True: A monitoring system that tracks temperature-sensitive shipments in real-time.
- DHL’s Life Sciences and Healthcare: A logistics solution utilizing data analytics and IoT sensors to ensure product integrity.
- Maersk’s Cold Chain: A refrigerated container shipping solution using IoT sensors and data analytics.
Technology has transformed cold chain logistics, enabling real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and optimized operations. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, ensuring the safe and efficient transportation of temperature-sensitive products.
Industries Relying on Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics plays a critical role in various industries, ensuring the safe transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive products. Let’s explore some of these industries and their reliance on cold chain logistics.
Pharmaceuticals
Imagine a patient awaiting a life-saving vaccine in a remote area. Cold chain logistics ensures the vaccine’s potency and effectiveness, maintaining the required temperature range during transportation and storage. Pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer, Merck, and GlaxoSmithKline rely on cold chain logistics to deliver vital medicines to patients worldwide.
Food and Beverages
Picture a consumer enjoying a fresh, juicy strawberry in winter. Cold chain logistics makes this possible, transporting perishable produce from farms to stores while maintaining optimal temperatures. Companies like Dole, Driscoll, and Nestle rely on cold chain logistics to deliver fresh food and beverages to consumers globally.
Biotechnology
Consider a researcher working on a groundbreaking cure for a rare disease. Biotechnology companies like Genentech, Biogen, and Gilead Sciences rely on cold chain logistics to transport temperature-sensitive biological samples, reagents, and medicines, ensuring the integrity of these critical products.
Additional Industries
Other industries relying on cold chain logistics include:
- Agriculture: Transporting perishable agricultural products, like meat and dairy products.
- Cosmetics: Ensuring the quality and safety of temperature-sensitive cosmetics and personal care products.
- Chemicals: Handling and storing temperature-sensitive chemicals, like certain solvents and reagents.
Real-Life Examples
- COVID-19 Vaccines: Cold chain logistics played a critical role in distributing COVID-19 vaccines worldwide, ensuring their potency and effectiveness.
- Organ Transplants: Cold chain logistics help transport organs for transplantation, maintaining optimal temperatures to preserve organ viability.
- Food Safety: Cold chain logistics ensures the safe transportation and storage of perishable food products, preventing contamination and foodborne illnesses.
Cold chain logistics is a vital component of various industries, ensuring the safety, quality, and effectiveness of temperature-sensitive products. As these industries continue to evolve, the importance of cold chain logistics will only grow, impacting lives worldwide.
Optimizing Cold Chain Logistics Operations
To ensure the efficient and effective transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive products, cold chain logistics operations must be optimized. Here are some guidance and real-life examples to help optimize operations:
Warehouse Management
- Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to ensure older products are shipped before newer ones.
- Use temperature monitoring systems to track warehouse conditions and prevent excursions.
- Train warehouse staff on proper handling and storage procedures.
Example: A biotechnology company implemented a warehouse management system that tracks inventory and monitors temperature conditions, resulting in a 25% reduction in product spoilage.
Route Optimization
- Use data analytics and mapping tools to identify the most efficient routes and reduce transit times.
- Consider using alternative modes of transportation, such as air or sea, for long-distance shipments.
- Implement a real-time tracking system to monitor shipments and make adjustments as needed.
Example: A pharmaceutical company optimized its route planning, resulting in a 30% reduction in transit times and a 20% reduction in transportation costs.
Contingency Planning
- Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies, such as backup power sources and emergency transportation plans.
- Establish a communication plan to notify stakeholders in the event of a disruption.
- Conduct regular training exercises to ensure staff are prepared for emergencies.
Example: A food manufacturer developed a contingency plan for natural disasters, which helped them quickly recover from a hurricane and maintain supply chain continuity.
Additional Optimization Strategies
- Implement a quality management system to ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards.
- Use data analytics to monitor and improve operations, such as tracking temperature excursions and transit times.
- Consider outsourcing logistics operations to a specialized third-party provider.
By optimizing cold chain logistics operations, companies can ensure the safe and efficient transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive products, ultimately protecting public health and safety.
Emerging Trends in Cold Chain Logistics
The cold chain logistics industry is evolving rapidly, driven by emerging trends such as sustainable practices, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands. Let’s explore these trends and their potential impact on the industry.
Sustainable Practices
- Reduce carbon footprint: Companies are adopting alternative fuels, electric vehicles, and eco-friendly packaging to minimize their environmental impact.
- Increase energy efficiency: Advanced insulation materials, solar-powered refrigeration, and energy-efficient warehouses are being implemented to reduce energy consumption.
- Waste reduction: Initiatives like recycling, composting, and minimizing food waste are gaining traction.
Example: A logistics company in the Netherlands introduced electric trucks for last-mile delivery, reducing CO2 emissions by 75%.
Technological Advancements
- IoT sensors: Real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and location enables proactive interventions and optimized logistics.
- Automation: Robotics and automation streamline warehouse operations, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency.
- Data analytics: Advanced data analysis improves route optimization, demand forecasting, and supply chain visibility.
Example: A pharmaceutical company in the US implemented IoT sensors to monitor temperature-sensitive shipments, resulting in a 90% reduction in product spoilage.
Changing Consumer Demands
- Increased demand for perishable goods: Consumers seek fresh, healthy, and exotic products, driving the need for efficient cold chain logistics.
- E-commerce growth: Online shopping requires fast, flexible, and reliable cold chain logistics to ensure product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Transparency and traceability: Consumers expect end-to-end visibility and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Example: An e-commerce company in China partnered with a logistics provider to offer same-day delivery of fresh produce, resulting in a 50% increase in sales.
Additional Emerging Trends
- Alternative transportation modes: Exploring options like drones, hyperloop systems, and high-speed rail to reduce transit times and emissions.
- Advanced materials: Developing new insulation materials, phase change materials, and advanced packaging solutions to improve temperature control and reduce waste.
By embracing these emerging trends, the cold chain logistics industry can reduce its environmental impact, increase efficiency, and meet evolving consumer demands, ultimately ensuring the safe and efficient transportation of temperature-sensitive products.

